What is Serverless & How Does it Work?
Serverless architectures help you build scalable, cost-effective applications faster. They remove the burden of operating your own servers and allow you to focus on developing your app instead of building out infrastructure. However, serverless architecture presents its own set of challenges and considerations that are unique from other architectures.
This guide will explain what serverless architecture is, why it’s beneficial, how it works, different types of serverless solutions, and the pros and cons of using this type of architecture in your next project.
What is Serverless Architecture?
Serverless architecture is a type of architecture where the developer does not have direct access to server-side code. Instead, they define a set of rules that dictate how the application will respond to certain events. In this way, serverless architecture is similar to event-driven architecture, with the key difference being that it also takes care of hosting and scaling the application itself.
In traditional architectures, developers use what is known as “colocation,” or locating their services on the same server where an application is hosted. In a serverless architecture, however, developers use “federation,” which means locating their services on different servers that are owned and managed by a third party.
Popular Serverless Frameworks and Services
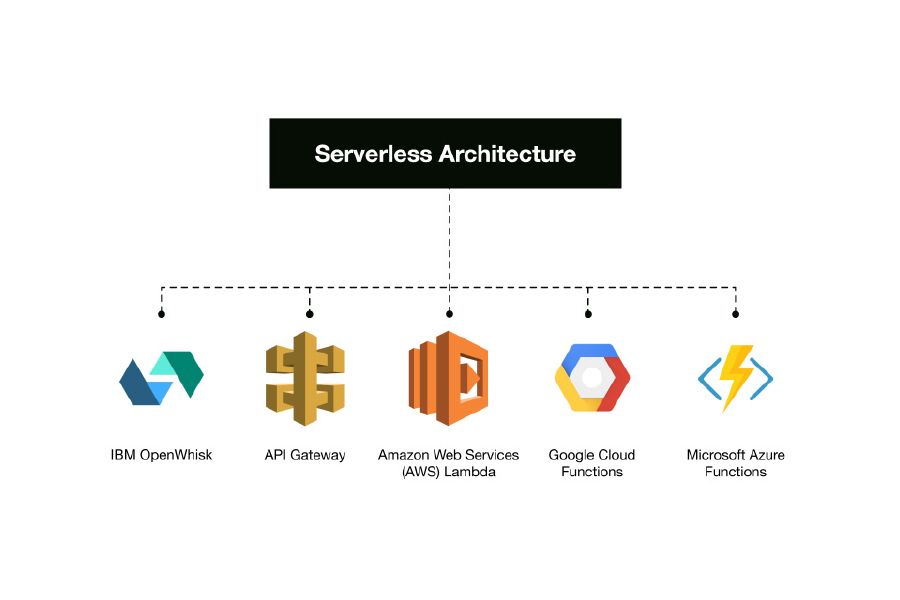
AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service provided by Amazon Web Services. It allows you to run code without provisioning or managing servers. You simply upload your code, and Lambda takes care of everything required to run and scale your code with high availability. It supports multiple programming languages like Java, Python, Node.js, C#, and more. AWS Lambda can be used for a variety of use cases like data processing, web back-ends, and IoT back-ends, among others.
AWS Lambda provides the following benefits:
- Serverless architecture: AWS Lambda will automatically scale up or down as needed without any additional configuration.
- Pay for only what you use: AWS Lambda charges you based on how much time your code spends running, not by the hour or minute.
- Flexible and easy to use: You don’t need to be an expert in server management; AWS Lambda takes care of all of that for you.
Check out our AWS Lambda Course:

Google Cloud Functions
Google Cloud Functions is a serverless computing platform that allows developers to run code in response to events without having to manage the underlying infrastructure. It is an easy way to build and run code without the need to provision servers, configure firewalls, or scale your computing resources. Google Cloud Functions can be invoked through HTTP requests and messages from other Google Cloud services like Pub/Sub.
Microsoft Azure Functions
Azure Functions is a serverless computing service provided by Microsoft Azure. It enables you to run code on-demand without the need to manage or provision servers. You can simply upload your code, and Azure Functions takes care of everything required to run and scale your code with high availability.
It supports multiple programming languages like C#, Java, JavaScript, Python, and more. Azure Functions can be used for a variety of cases, such as web and mobile back-ends, data processing, and IoT, among others. You can trigger Azure Functions through various events like HTTP requests, messages from other Azure services like Event Grid, or timer-based triggers.
IBM Cloud Functions
IBM Cloud Functions is a serverless computing platform provided by IBM Cloud. It allows you to write and run code in response to events without the need to manage or provision servers. You can upload your code, and IBM Cloud Functions handles everything required to run and scale your code with high availability.
It supports multiple programming languages like JavaScript, Python, Java, Swift, and more. IBM Cloud Functions can be used for various cases, such as web and mobile back-ends, data processing, and IoT. You can trigger IBM Cloud Functions through various events like HTTP requests, messages from other IBM Cloud services like Message Hub, or timer-based triggers.
API Gateway
An API Gateway is a server that acts as an entrance to your serverless ecosystem. It manages all the requests received from clients, routes them to the appropriate microservices, and returns the results. In other words, API Gateway acts as a reverse proxy and provides a single point of entry for all your microservices.
It also provides additional functionalities like security, rate limiting, caching, and request/response transformations. API Gateway helps to decouple the client applications from the backend services, making it easier to manage and scale the microservices. It also simplifies client-server communication by providing a unified API interface and handling all the complexities behind the scenes.
Why use a Serverless Architecture?
Below are the reasons why organizations choose serverless architecture:
- Cost-effectiveness: Serverless architecture allows you to pay only for the resources you use, which can significantly reduce costs.
- Scalability: Serverless architecture enables you to scale your application automatically based on demand without worrying about managing the underlying infrastructure.
- Reduced time to market: With serverless architecture, you can focus on developing your application logic without worrying about the infrastructure, which can help you bring your product to market faster.
- Increased flexibility: Serverless architecture allows you to use multiple programming languages, platforms, and services, which can increase your flexibility in terms of development and deployment.
- Improved reliability: Serverless architecture provides built-in redundancy, which increases the reliability of your application. Additionally, it reduces the risk of downtime due to hardware or software failures.
Overall, serverless architecture can help you reduce costs, increase scalability, and improve the reliability of your application.
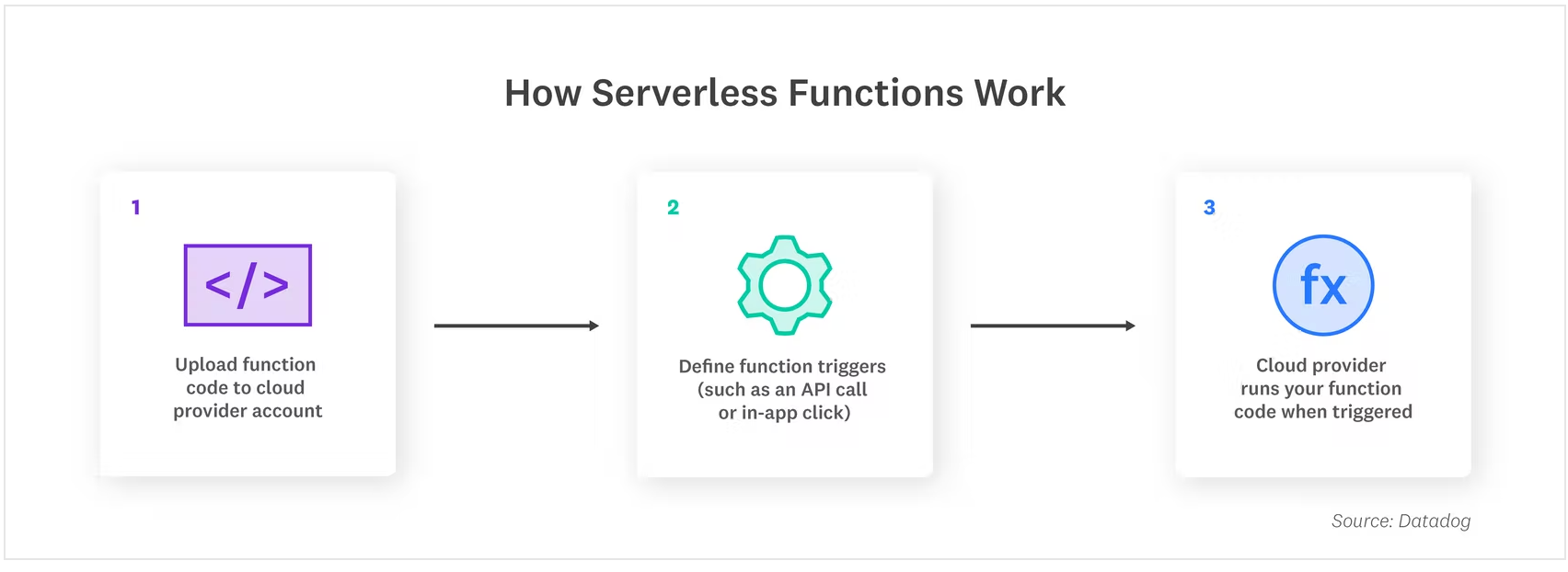
How does a Serverless Architecture work?
Serverless architectures rely on a third-party service to execute your code. While many services like AWS Lambda and Google Cloud Functions provide services that let you execute your code, many others let you store and analyze data, send emails, etc. This is one of the biggest benefits of serverless architecture: you can use a single service to do many things.
In the case of AWS Lambda, for example, your code will run in a container that is isolated from other containers. This means that a single function cannot essentially “infect” other functions with its state, which makes it easier to scale and maintain your application.
Managing servers is not an easy task; it takes a lot of time and resources. In addition, teams must maintain server hardware, software, and security updates, as well as backup data in case of failure. Developers can ditch these burdens to a third-party provider by using serverless architecture and concentrate on writing application code rather than wasting time on maintaining the underlying server-related infrastructure.
Function as a Service (FaaS) is one of the most popular and widely used serverless architectures. The function performs a specific task when triggered by an event configured by developers - such as an email or HTTP request. When a function is triggered, the cloud provider either executes the function on an existing server or, if there is no server active, spins up a new instance.
Different Types of Serverless Solutions
There are many different types of serverless solutions, including both managed and un-managed offerings. They often integrate with other services like databases, CRMs, messaging systems, and more to allow for greater scalability and flexibility. This can make serverless architecture even more attractive to businesses.
- Managed services - Managed services are hosted and managed by a third-party service. An example of this type of service is AWS Lambda, which lets you run code without worrying about infrastructural concerns.
- Self-hosted services - Self-hosted services are those that you host and manage yourself.
Benefits of a Serverless Architecture
Here are the benefits of serverless architecture:
- Scalability - Because you are only paying for the resources you use and there is no fixed cost to your architecture, you can scale your app to meet sudden increases in demand.
- No downtime - Because you are not managing your own servers, you don’t have to worry about them crashing and causing your app to go down with them.
- No or low maintenance - As a developer, you don’t have to worry about patching your servers or ensuring that your apps are running smoothly.
- Resource efficiency - Because every serverless solution has built-in scaling mechanisms and uses only what it needs, you can be sure that you are not over-provisioning your resources.
- Quick development - You can develop your app quicker because you don’t have to worry about setting up your own servers and can focus instead on your code.
Disadvantages of a Serverless Architecture
Below are the drawbacks of serverless architecture:
- Data governance - Because you do not control the servers where your code is running, you do not have full control over how your data is governed. This can be especially true in unmanaged solutions, as you have no control over the servers themselves.
- Security - Because your code is running on someone else’s servers, you cannot fully secure it. While most managed services have some sort of security features built in, unmanaged solutions do not.
- No direct access to the hardware - Because you are not hosting your code on your own hardware, you have no direct access to the infrastructure powering it. This can lead to issues if you need to make modifications to your code.
- Less control over scalability - Because managed services can scale your code for you, you don’t have complete control over your application’s scalability.
Conclusion
Serverless computing has been around for a while, but it has grown in popularity over the last few years. It is a cost-effective and scalable solution for companies that have a lot of traffic and need to handle more requests at once. The serverless architecture is also perfect for companies with unpredictable traffic patterns, as they don't need to spend money on expensive servers when they don’t have any traffic at all.
Learn serverless from different cloud providers at our playgrounds.
Playgrounds provide instant access to sandboxed Cloud or DevOps environments for you to play around and have a complete understanding of how things work practically.
More on DevOps:

