☁️ In 2025, cloud computing is not just a tech trend – it’s the backbone of modern IT careers.
Nearly all companies now leverage cloud services in some form (around 96% of enterprises use public cloud — Source: spacelift.io), driving enormous demand for cloud-skilled professionals.
Global spending on cloud tech is surging — forecasted to reach $675 billion in 2024, up from $561 billion in 2023 (Source: force4.co), and by 2025, half of the world’s data is expected to reside in cloud environments (Source: armapartners.com).
Cloud computing skills are no longer optional—they are foundational for driving innovation and staying competitive in today’s technology landscape.
Cloud empowers remote and hybrid work (accessing systems anytime, anywhere), enables real-time collaboration, and fuels digital transformation across industries. For tech professionals, students, career switchers, and hiring managers alike, understanding cloud career paths and opportunities is now a crucial step toward success.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the major cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and why they matter, outline cloud career paths for beginners through senior experts, discuss top certifications (AWS, Azure, GCP), and highlight the importance of hands-on learning with labs and projects. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to advance into leadership, this guide will help you navigate the skyward rise of cloud computing in 2025 with confidence and inspiration.
Cloud Service Models Explained: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
Cloud services come in different flavors. The three primary models to know are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
Understanding these models is fundamental, as they define how you use cloud and inform what skills you need.
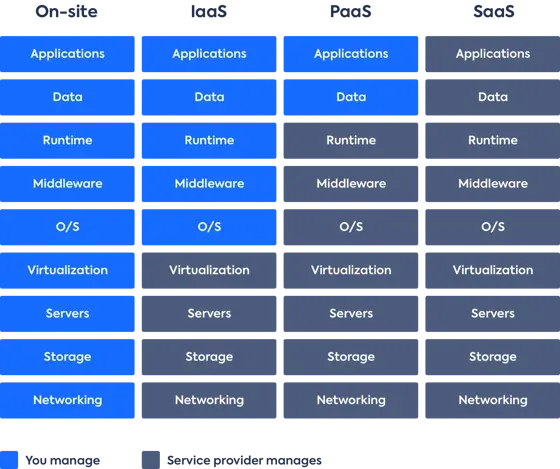
📊 Figure: On-premises vs IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS – Who manages what in each model.
In on-site data centers, you manage everything.
In IaaS, the cloud provider manages virtualization, servers, storage, and networking, while you manage the rest.
In PaaS, the provider also manages the operating system, middleware, and runtime, leaving you to handle just data and applications.
With SaaS, the provider manages the entire stack and delivers a complete application to you.
Source: leanix.net
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS = Renting virtual infrastructure — You get access to computing resources like VMs, storage, and networking, but you manage the OS, runtime, and applications on top of it.
🛠️ You manage: OS, runtime, app configuration
☁️ Cloud provider manages: Hardware, virtualization, storage, and network
🔍 Example: Launching an EC2 instance on AWS or an Azure VM where you install and configure your own software stack.
📌 Key Highlights:
- 🔧 Full control over the OS and software stack
- ⚙️ Best for lift-and-shift of traditional workloads
- 💸 Pay-as-you-go pricing for compute, storage, and network
- 🌐 Ideal for custom environments and flexible setups
📈 Why It Matters: IaaS fundamentals are crucial for cloud support engineers, sysadmins, and solution architects. Mastering VMs, security groups, storage, and networking is key in many cloud jobs.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS = Deploy code without managing infrastructure — The cloud provider handles the OS, middleware, and runtime. You only manage the app code and data.
🛠️ You manage: Application code, data
☁️ Cloud provider manages: OS, runtime, servers, scaling, provisioning
🔍 Example: Use AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, or Azure App Services to deploy apps. The platform auto-scales and handles provisioning.
📌 Key Highlights:
- ⚙️ Simplified app deployment – no need to manage OS or runtime
- 🧰 Comes with built-in services (databases, auth, monitoring)
- 📦 Ideal for scalable web and mobile app development
- ⚡ Speeds up innovation by focusing only on code
📈 Why It Matters: PaaS is perfect for developers and cloud engineers building modern apps. It’s widely used in DevOps workflows and makes CI/CD pipelines and scalable design easier to implement.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS = Ready-to-use cloud applications — The provider manages the entire stack: infrastructure, OS, platform, and application. You just access the software via web or API.
🛠️ You manage: Nothing (except maybe users and settings)
☁️ Cloud provider manages: Everything — hardware, platform, app updates, and scaling
🔍 Example: Tools like Gmail, Salesforce, Zoom, or Office 365 — instantly available via browser or API with zero infrastructure management.
📌 Key Highlights:
- ⚡ Fastest time-to-use — no setup or deployment required
- 🔐 Managed security, uptime, scaling, and updates
- 🧩 Ideal for end-users, business teams, or integration scenarios
- 📊 Popular in enterprise for productivity, CRM, email, etc.
📈 Why It Matters: Cloud professionals often integrate, secure, and manage SaaS tools in an organization. Understanding SaaS helps you design secure, efficient cloud ecosystems with the right balance of build vs. buy.
Each model has its place – IaaS for flexibility, PaaS for developer productivity, SaaS for ready-to-use solutions. As a cloud professional, being aware of these models and when to use each is critical. Many companies adopt a mix (for instance, using IaaS for custom legacy systems, PaaS for new applications, and SaaS for standard business apps). Knowing the differences will also help you in interviews and on the job when discussing cloud strategy.
Entry-Level (Freshers): Launching Your Cloud Career
For newcomers to tech or recent graduates, the cloud domain can be exciting yet overwhelming. The good news is that beginner-friendly paths exist to get you started. Here’s a roadmap to launch a successful entry-level cloud career:
Step 1: Learn the Basics
Your journey starts with understanding core IT concepts: networks, servers, and databases.
Understand cloud-specific topics like:
- Virtualization and scalability
- Regions, zones, and redundancy
- Basic cloud security principles
Begin with vendor-neutral courses or introductory ones from AWS, Azure, or GCP.
Pro Tip: Try AWS, Azure, or Google’s Cloud 101 — free and beginner-friendly.
Step 2: Earn an Entry-Level Certification
Choose beginner-friendly certifications such as:
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner
- Microsoft Azure Fundamentals (
AZ-900) - Google Cloud Digital Leader
These validate your understanding of broad cloud concepts.
Why it matters: Certified learners report up to 27% salary boosts after certification!
Even if it's not a job guarantee, it’s a major credibility booster.
Step 3: Get Hands-On with Free Tiers
Sign up for free-tier accounts on:
- AWS
- Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Practice tasks like:
- Launching cloud servers and websites
- Storing data in cloud databases
- Writing serverless functions (like Lambda)
Remember: These environments are built for trial and error — break stuff and learn!
Step 4: Build a Portfolio of Projects
Save and share every hands-on project you build. Ideas:
- Host a web app on AWS
- Use Terraform or CloudFormation to deploy infrastructure
- Build a simple CI/CD pipeline
Document everything on:
- GitHub – for code & infra
- Blog – explain what you built & why
Why? It shows employers you can do things, not just talk about them.
Step 5: Gain Experience (Even Small Projects Count)
Experience doesn’t require a "cloud engineer" title. Look for:
- Hackathons
- College/bootcamp projects
- Freelance gigs
- IT support or dev roles with cloud touchpoints
Internships or co-ops that involve cloud are gold for students.
Switching fields? Highlight anything cloud-related from past roles (e.g., database migrations).
Step 6: Network with Others in the Field
Join communities like:
- Cloud forums (Reddit, Stack Overflow)
- Discord servers for learners
- LinkedIn groups and conversations
Attend webinars, meetups, or cloud study groups.
Message professionals on LinkedIn — comment on their posts, ask questions.
Over time, your network will:
- Refer you to roles
- Mentor you
- Help you stay updated on cloud trends
🎯 Target Roles After This Roadmap
With these steps completed, you’ll be well-prepared for junior cloud positions that offer real-world experience and hands-on learning. Common entry-level job titles include:
- Cloud Support Associate
- Junior Cloud Engineer
- DevOps Technician
- Cloud Operations Analyst
💡 These roles often involve:
- Monitoring cloud systems and infrastructure
- Responding to alerts and incidents
- Writing simple automation or deployment scripts
- Assisting with CI/CD pipelines and service rollouts
🔑 Why it matters: These are excellent launching pads where you’ll learn from senior engineers, gain confidence, and build real project experience. The goal is simple: get your foot in the door and grow from there.
Mid-Level Professionals: Accelerating Your Cloud Journey
If you have a few years of experience in IT or software development and some exposure to cloud, you fall into the mid-level category. At this stage, you’ve likely mastered the basics and perhaps even worked on some cloud projects. Now it’s time to accelerate your cloud career and position yourself for senior roles. Here are key strategies for mid-level cloud professionals:
Leverage Your Existing Skills
Use your background! Developers can pivot to cloud-native apps or DevOps automation. Sysadmins and network engineers? You’re set up for cloud infrastructure, migrations, and reliability roles.
For example, a Python dev might build AWS Lambda functions or Terraform scripts. A sysadmin could become a Cloud Engineer managing AWS or Azure infrastructure.
This approach reduces the learning curve and shows employers how you apply existing skills in a cloud context.
Specialize (or Diversify) in a Cloud Role
Mid-career is the perfect time to either specialize or stay broad:
- Specialist: Cloud Engineer, Cloud Developer, Cloud DevOps, Cloud Security
- Generalist: Cloud Solutions Engineer working across domains
Want even more marketability? Learn a second cloud like Azure or GCP to go multi-cloud.
Pursue Advanced Certifications
Move beyond entry-level certs. Target mid-pro certs like:
AWS Solutions Architect – Associate,DevOps Engineer – ProAzure Administrator Associate,Solutions Architect ExpertGoogle Associate Cloud Engineer,Professional Cloud Architect
Cert prep not only boosts your resume, it fills knowledge gaps and sharpens your real-world skills.
Lead Cloud Projects
Take ownership. Lead a cloud migration, container rollout, or cost optimization project.
You don’t need an official “lead” title to lead — be the initiative-taker, documenter, and coordinator. Every win becomes a story for interviews and reviews.
Mentor and Collaborate
Mentor juniors, run brown-bag sessions, or write internal guides. Teach to reinforce your own knowledge.
Contribute to open-source or internal tooling. Being collaborative and visible grows your influence — and your readiness for future leadership roles.
Keep Learning Continuously
Cloud evolves fast — new services, new paradigms (like edge computing, WASM, new K8s features).
Block weekly time to learn. Follow blogs, attend webinars, or master new tools like Kubernetes, Docker, Terraform, etc. Continuous learners rise faster.
Career Trajectory & Goals
Where to next?
- Cloud Architect – design systems and security across teams
- Cloud Team Lead – mentor, manage, and guide projects
- Cloud Consultant – guide companies across industries
Think big-picture: How can cloud solve business problems? That’s the mindset that gets you promoted.
Mid-Level: Your Most Transformative Stage
Mid-level is often the most transformative stage of a cloud career – you move from executing tasks to designing, leading, and strategizing. It’s a time to accelerate your growth by specializing, certifying, and stepping up to leadership challenges.
With a few solid projects under your belt and advanced skills, you’ll be well on your way to expert status.
Senior Professionals: Thriving in Cloud Leadership
For seasoned experts with 8+ years in the tech industry (and likely several years of cloud experience), the cloud career path shifts toward strategic leadership and specialized expertise. Senior cloud professionals are the architects of big-picture solutions and the captains steering enterprise cloud initiatives. Here’s how to thrive at this advanced stage:
Think Strategic and Business-Oriented
Move beyond technical implementation. Focus on aligning cloud projects with business goals like growth, cost savings, and customer experience.
Design enterprise-level solutions that are scalable, secure, and cost-efficient. Shift your mindset from “how do I use this tech” to “how does this tech drive business value?”
Examples: Lead a cloud migration roadmap that cuts IT spend, or ensure company-wide cloud compliance and risk management.
Specialize in Niche Domains
While mid-level pros generalize, senior leaders often own a niche. Choose an in-demand area like:
- Cloud Security
- AI/ML services on cloud
- IoT, Kubernetes at scale, or Cost Optimization
Become the go-to expert. This boosts your visibility and opens doors to principal or advisory roles. Consider specialty certifications like AWS Security or Machine Learning.
Lead Teams and Foster Innovation
Build your leadership brand. Lead cloud teams, mentor others, and champion best practices.
Start a Cloud Center of Excellence, pilot new technologies, or manage org-wide architecture standards.
Own major cloud initiatives – like launching a new cloud-native product – and coordinate across teams and stakeholders.
Stay Current and Embrace Emerging Tech
Don’t let your skills stagnate. Stay sharp with trends like edge computing, serverless, multi-cloud orchestration, and AI integration.
Attend advanced cloud events (e.g., AWS re:Invent, GCP Next), block time for R&D, and experiment with new tools.
Being future-focused ensures you can guide your org into the next generation of cloud strategies.
Become a Thought Leader
Share what you know. Blog, speak, teach, or publish real-world case studies. Build your reputation and attract new opportunities.
Topics like multi-cloud optimization or fintech cloud security are gold. Contribute to open-source or influence cloud product features.
This builds credibility and strengthens your personal brand.
Aim for Executive Cloud Roles
Chart your path to Principal Architect, Cloud Practice Manager, or even CTO for Cloud.
Start participating in strategic planning and cloud budget conversations. Learn to present ROI-backed proposals (e.g., “Refactoring to serverless will save $X over 2 years”).
Develop soft skills like executive presence, empathy, and negotiation. Whether you pursue an MBA or gain experience on the job, position yourself as a decision-maker.
In Summary: Be the Strategic Leader
Senior cloud professionals combine technical excellence with strategic vision. You’re the bridge between C-suite goals and technical implementation – a role that shapes your organization’s cloud destiny.
It’s a career path of great impact and reward: salaries often reach into the six-figure range (e.g., Cloud Engineers average $123,000–$194,000/year), and the challenges you solve are meaningful at scale.
By staying adaptable, mentoring others, and keeping business outcomes in focus, you’ll continue to thrive as a cloud leader in 2025 and beyond.
Cloud Certifications: AWS, Azure, and GCP Options
No matter your career stage, certifications are a powerful tool in the cloud career toolkit. They provide a structured learning path, validate your skills to employers, and can boost your confidence (and sometimes your salary). In fact, as noted earlier, a large majority of cloud pros see tangible benefits – 73% of AWS certified folks reported a pay increase, averaging 27% more, after earning their cert. Employers use certifications to identify skilled candidates and to upskill their teams internally. Let’s break down the major cloud provider certification paths and how they can fit into your career development:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Certifications
🔸Why AWS?
AWS is the largest public cloud provider — and its certification path is one of the most recognized in the industry.
Start Here: Foundational Level
🟢 AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner
- Covers AWS basics and cloud concepts
- Ideal for beginners or non-tech professionals
- Great first step before deeper certs
💡 Recommended for: Anyone new to cloud or AWS
Next Step: Associate-Level Certifications
💡 Choose one based on your role or interests. Solutions Architect – Associate is a safe and valuable choice for most paths.
Advanced Level: Professional Certifications
🔒 These are tough! Best for those with real-world experience managing large-scale AWS environments.
🎯 Go Deep: Specialty Certifications
Choose a specialty if your role is focused in a specific domain:
💬 Which Certification Should You Choose?
- 👶 Beginner? Start with Cloud Practitioner
- 🧱 Building Experience? Go for Solutions Architect – Associate
- 👨💻 Developer? Pick Developer – Associate
- ⚙️ Ops/Infra? Choose SysOps Administrator – Associate
- 🏗️ Seasoned Cloud Pro? Go Professional level
- 🎯 Role-Specific? Pick a Specialty cert
🏁 Final Note
These certifications are:
✅ Recognized industry-wide
✅ Resume-boosters
✅ Aligned to real-world roles
Whether you’re just starting or going pro, there’s an AWS certification designed to fit your journey.
Microsoft Azure Certifications
🔹 Why Azure?
Microsoft Azure has a role-based certification framework and is widely adopted by enterprises across the globe. In some regions, Azure even outpaces AWS in adoption.
Start Here: Foundational Level
🟦 Microsoft Azure Fundamentals (AZ-900)
- A broad introduction to Azure cloud services and concepts
- Great for those completely new to Azure or cloud computing
- Helps build confidence before moving into role-specific tracks
💡 Recommended for: Beginners, career switchers, and non-technical roles wanting cloud literacy
Next Step: Associate-Level Certifications
Choose the cert that best aligns with your current or target role:
💡 Tip: Pick the associate-level cert that mirrors your job role or the one you're aiming for.
Advanced Level: Expert Certifications
💡 Note: These expert-level certs are highly respected and signal strong architecture or DevOps mastery.
💬 How Should You Proceed?
- 👶 New to Azure? Start with AZ-900 (Fundamentals)
- 🛠️ Admin Role? Go for AZ-104 (Administrator)
- 👨💻 App Developer? Choose AZ-204 (Developer)
- 🔐 Security-Focused? Get AZ-500 (Security Engineer)
- 📊 Data Professional? Pick DP-203 (Data Engineer)
- 🏗️ Want to go deeper? Aim for Solutions Architect Expert
- 🚀 Doing DevOps on Azure? Go for AZ-400 (DevOps Engineer Expert)
🏁 Final Note
Azure certifications are:
✅ Enterprise-trusted
✅ Role-specific and practical
✅ A clear path to growth in Azure careers
They show that you speak Azure’s language — and can design, build, secure, and manage cloud solutions at scale.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Certifications
🔹 Why GCP?
Google Cloud's certification tracks are shorter but highly practical. Exams are known for their real-world scenario-based questions and hands-on orientation.
Start Here: Foundational Level
☁️ Cloud Digital Leader
- Covers general cloud concepts and Google Cloud basics
- No hands-on experience required
- Ideal for beginners, business leaders, and non-technical professionals
💡 Recommended for: Managers, product teams, or anyone new to GCP
Associate Level: First Hands-On Certification
💡 Tip: This is the most popular entry cert for hands-on learners targeting GCP roles.
Professional Level: Role-Based Certifications
💡 Note: GCP Professional certs expect broad knowledge of Google Cloud's services and how to integrate them effectively.
💬 Choosing GCP Certifications
- 👶 Beginner? Start with Cloud Digital Leader
- 🛠️ Ready to get hands-on? Take Associate Cloud Engineer
- 🏗️ Want to design solutions? Go for Professional Cloud Architect
- 📊 Working with data? Choose Professional Data Engineer
- 👨💻 Building cloud apps? Pick Professional Cloud Developer
- 🚀 Focusing on DevOps? Go for Professional DevOps Engineer
- 🔐 Security-focused? Take Professional Security Engineer
🏁 Final Note
GCP certifications are:
✅ Focused on real-world skills
✅ Valuable in multi-cloud or GCP-heavy environments
✅ Less common – which helps you stand out in a sea of AWS/Azure resumes
If your company uses GCP, getting certified could give you a major edge.
Are Certifications Worth It?
Absolutely – but with a caveat: Certifications are powerful tools when used to complement hands-on experience, not replace it.
Use certification prep as a structured learning path, but make sure you're also applying those concepts in the real world or lab environments.
⚠️ Don’t overdo it: It’s better to have 2–3 well-aligned certifications + solid project experience than to hold 10 certs with no practical exposure.
That said, certifications can:
- ✅ Help you land interviews (many employers and HR filters check for them)
- ✅ Accelerate promotions or career switches
- ✅ Boost your confidence — proving you can solve cloud problems under pressure
💡 Bottom Line: Learn by doing, and let certifications validate that journey — not define it entirely.
Hands-On Learning: Labs, Projects, and Cloud Playgrounds
One Principle Stands Above All:
Hands-on experience is indispensable in the cloud world. No matter how many certifications or theories you know — what truly builds skill, confidence, and credibility is real, practical application.
Cloud computing is very much a “learn by doing” domain. You can read and watch tutorials for months, but nothing beats actually rolling up your sleeves and working in a cloud environment. Here we emphasize why practical learning matters and how to go about it (with some resource recommendations):
🧪 Why Hands-On Matters
Cloud platforms are vast and continually evolving – the best way to truly understand how they work is to use them. When you set up infrastructure or troubleshoot an app in the cloud, you gain insights you simply can’t get from theory.
Employers know this; that’s why so many job postings list “hands-on experience with [XYZ]” as a requirement.
By practicing with labs and projects, you internalize skills like:
- Navigating AWS, Azure, or GCP consoles
- Writing infrastructure-as-code
- Configuring security groups
- Adjusting auto-scaling parameters
Yes, you’ll make mistakes — maybe even rack up a small bill — and that’s good. That’s how you learn to fix things. Hands-on work builds real confidence.
🧪 Use Free Resources and Sandboxes
When learning, leverage free or low-cost environments so you don’t worry about “breaking” anything.
Cloud free tiers are live environments you can play in. Additionally, many platforms and third-party providers offer sandbox labs — temporary, pre-configured environments made for learning.
Examples of hands-on sandbox projects:
- Deploy a WordPress site on a cloud VM
- Set up a small Kubernetes cluster with a demo app
- Write a Terraform script to provision an S3 bucket and test it
Be curious. Ask: “What happens if I change this setting?” — then try it and see.
🛠️ Structured Labs and Exercises
Follow structured lab guides or tutorials that walk you through projects step-by-step.
Most major cloud platforms offer their own labs:
- AWS – Official Training and Certification labs
- Azure – Microsoft Learn Modules
- GCP – Google Cloud Skills Boost
As you grow, move to challenge labs (goal is provided, but you figure out the steps). Platforms like Qwiklabs, Cloud Academy, and A Cloud Guru offer excellent practice environments.
🚀 KodeKloud’s Learning Paths and Playgrounds
KodeKloud is a top hands-on learning platform for DevOps and cloud professionals.
- Learning Paths – Structured programs for DevOps, Cloud Engineers, and more
- Interactive Labs – Practice as you learn with guided scenarios
- Cloud Playgrounds – Use AWS, Azure, and GCP in-browser without setup or cost
You can launch EC2 instances, configure Azure VNets, or test Kubernetes setups — all inside a safe, zero-risk environment.
💡 Visit KodeKloud’s site to explore Learning Paths and Playgrounds.
📦 Build Real-World Projects
Aside from guided labs, work on self-driven projects from start to finish.
Project Ideas:
- Deploy a full-stack ToDo app on AWS (React + Node.js + DynamoDB)
- Write an Ansible playbook or Terraform module to provision infrastructure
- Extend tutorials by adding new services, monitoring, or autoscaling features
These projects give you real exposure and portfolio material you can showcase to potential employers.
🤝 Join Cloud Learning Communities
Learning hands-on is more fun and effective with others.
Join:
- Discord servers and Reddit groups (like r/aws, r/devops)
- Slack communities with #cloud channels
- Webinars, meetups, or virtual hackathons
Engaging with others provides motivation, new ideas, and quick help when you're stuck. Many projects and solutions are born in community discussions.
🔗 Join the KodeKloud Community – Connect with others, ask questions, and learn from experts!
Join NowRemember, cloud expertise is ultimately proven by what you can do, not just what you know on paper. Every lab you tackle or project you build is a step closer to mastery. Also, hands-on learning tends to stick – the scenarios you encounter in practice (a strange error, a clever workaround, a performance tuning) become stories and lessons you carry into job interviews and real work situations. In the rapidly changing cloud landscape, cultivating the habit of continuous experimentation will keep your skills sharp. So spin up that test environment and start tinkering!

Continuous Learning and Growth
As we conclude this Cloud Career Guide, one overarching piece of advice bears repeating: never stop learning. The cloud computing field in 2025 is always evolving — what’s cutting-edge today might be standard tomorrow. The most successful cloud professionals embrace a mindset of continuous improvement. Stay curious and proactive in updating your skills. Make it a habit to learn about new services, read case studies of cloud architectures, or play with that new tool everyone’s talking about. Even at senior levels, the journey of learning never really ends (that’s part of what makes this field exciting!).
Equally important is to build real-world skills and stay hands-on throughout your career. Design personal projects, contribute to open source, or home-lab your crazy ideas. This keeps your knowledge fresh and applicable. If you’re in a management position, allocate time to remain technically adept; if you’re just starting, never shy away from a chance to get your hands dirty in code or config.
Finally, remember that a cloud career isn’t just about technology – it’s about people and solving problems. Engage with the community, share knowledge, and help others on their path. Networking and mentorship can open as many doors as technical brilliance. Communicate your ideas and celebrate teamwork, because cloud solutions often span multiple teams and disciplines.
Motivation and mindset will carry you a long way. Be adaptable, be resilient (setbacks like exam failures or tough outages happen – learn from them), and keep your passion for technology alive. The cloud domain offers exciting opportunities at all levels, with high demand and rewards for those who commit to it. Whether you’re aiming to become a sought-after Cloud Architect or just land your first cloud engineer job, keep pushing forward one step at a time.
In summary, the cloud is here to stay and will only expand in scope. By following the guidance in this guide – understanding core services, progressing through appropriate career milestones, earning certifications, and continually practicing your craft – you are setting yourself up for success in the cloud computing universe. Cloud careers are a marathon, not a sprint, but with continuous learning, hands-on projects, and active networking, you’ll be well-prepared to thrive for the long term.
🚀 Take the Next Step in Your Cloud Journey
Get your free copy of The Ultimate Cloud Career Growth Handbook by KodeKloud.
📥 Download Now














Discussion